
common interests and common objectives are not necessary for society.It is a network of social relationships which cannot see or touched.There can be more than one community in a society.It includes every relationship which established among the people.The dipole moment of an electric dipole is defined as the product of the two equal charges and perpendicular distance between them i.e. A uniform electric field is an ideal case in which the electric field lines are parallel with one another, for example between the plates of a large, parallel plate air capacitor. The number of electric lines of force passing through an area held perpendicularly is called electric flux.Įlectric lines flux can be defined as the scalar product of electric flux intensity and vector area. The electric field intensity (volts/meter) at any location is the force (Newtons) that would be experienced by unit test charge (Coulombs) placed at the location. The electric field intensity of a point due to a number of a charge is equal to the vector sum of an electric field intensity of individual charge. Electric Flux Formula: E Electric flux E Electric field A Area of the surface Q electric charge inside the surfaces of A 0 permittivity of free.

The electric field intensity of a point inside the electric field of a charge is the force experienced by a unit positive charge (+1 coulomb) placed at that point. The region around a charge where its electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion can be experienced is called an electric field of that charge.
ELECTRIC FIELD INTENSITY FREE
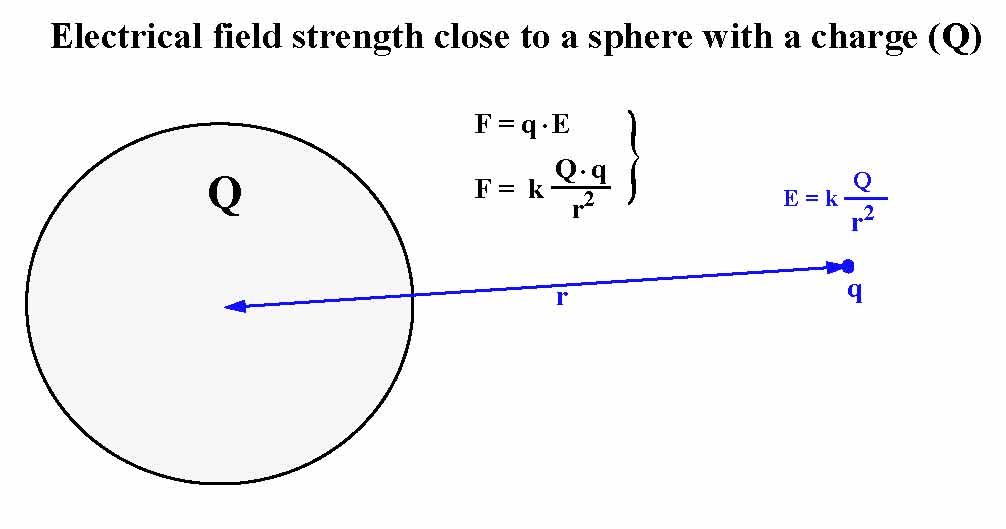
The dielectric constant or relative permittivity of a medium can be defined as the ratio of the permittivity of a medium and the permittivity of vacuum of free space. The dipole moment exists only when the positive and negative centres are separate.Ĭoloumb's law states that "the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges is directly proportional to the product of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them." The dipole moment of an isolated atom is zero because the centre of positive and negative charge coincides. The dipole moment of an electric dipole is defined as the product of the two equal charges and perpendicular distance between them i.e. Two equal and opposite charges separated at certain finite distance constitutes electric dipole. What is the magnitude of the electric field intensity at a point where a proton experiences an electrostatic force of magnitude 2. Hence, electric lines flux can be defined as the scalar product of electric flux intensity and vector area. system and charges present in the air or Vaccum Here, K is the proportionality constant whose value depends upon the medium in which charges are present and the system of a unit chosen.įor S.I. It states that "the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges is directly proportional to the product of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them."įigure: Two charges separated by a distance r apart. Because an electric charge experiences a force if it is in the vicinity of a charged body, there is an electric field surrounding the charged body ( see illustration).Electric Field Intensity and Electric Flux Coloumb's LawĬoloumb's Law is applied to calculate the force of attraction or repulsion between two-point charges. The SI unit of an Electric field is N/c or Newton/Coulomb. Again, if a voltage V exists across a distance r, then the electric field is defined as. The magnitude and direction of the electric field are expressed by the value of E, called electric field strength or electric field intensity or simply the. Coulomb’s law defines this electric field intensity formula. An electric field (or electrostatic field) exists in a region if an electric charge at rest in the region experiences a force of electrical origin. This is the electric field experienced by charge Q due to charge q.

In addition to electrostatic fields produced by separations of electric charges, electric fields are also produced by changing magnetic fields.Ī condition in space in the vicinity of an electrically charged body such that the forces due to the charge are detectable. Find step-by-step Engineering solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: The electric field intensity, E(z), due to a ring of radius R at. An electric field is a condition in space where the forces due to an electric charge in the vicinity of a charged body are detectable.Įlectric fields, along with magnetic fields, are a manifestation of the fundamental force known as electromagnetism.Įlectric field intensity, or field strength, is a vector characterizing the amount of force per unit charge.įor an assembly of charges, the resultant field is, by the principle of superposition, the vector sum of the field components due to the individual charges.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
